Isn’t it a wonderful thing when we can bring fiction to life? The movie Starwars highlights a device that is able to draw water from the air- a “vaporator”. Science and technology are now closer to making this object of fiction a reality.
Researchers from Xianming “Simon” Dal’s lab at the University of Texas at Dallas are working on technology that is able to extract water from the atmosphere.
According to their paper in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, there is a more effective way to harvest water that lends its origins from carnivorous plants.
This technology is far from ready for use, but the researchers are hopeful to manufacture a way for people to access safe and clean water, especially during shortages. Sixty-two percent of Texas experienced an extreme in August. It is common for Triple-digit temperatures to cause heat waves, and droughts, resulting in water shortages.
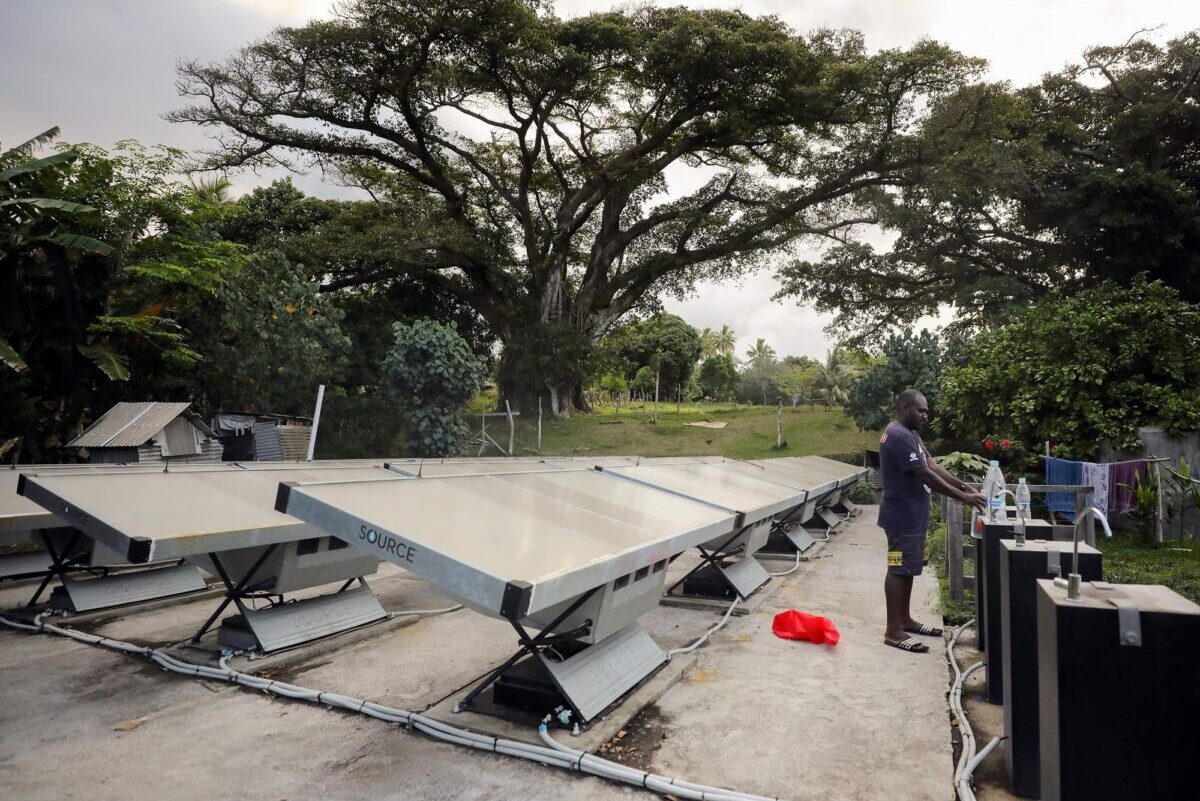

Decentralised distribution of water can help in preventing water shortages in drought-prone areas. The researcher has studied the harvesting of water for about ten years to create unlimited access to clean water by condensation.
The condensation process can be explained by what happens to a glass of cold water on a hot day. There is an interaction between the warm vapour in the atmosphere and the cold. The warm vapour cools down in contact with the glass and condenses into water droplets that collect on the surface of the glass. This is the method that Dai and his research team use in their attempt to harvest water from the air.
One limitation of water harvesting is that after the formation of the water droplets, there is nowhere for them to go. As a result, they accumulate, preventing new droplets from forming. Dai and his team were able to solve this conundrum by taking a cue from the way carnivorous plants devour insects.
During the harvesting process, the lubricated water droplets slide into small T-shaped channels creating more surface area for condensation to occur.
The project promises to be of immense use as it will provide a way for limitless access to clean water.